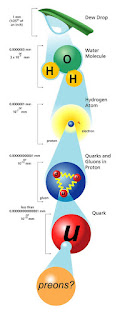
Size comparison (From the smallest known object to the biggest measured object)
we're going to look at the smallest known object ever found which is a Preon to the observable universe which is the biggest measured object. Sorry, to all my viewers who were waiting for my post for so long, but believe me I was working on a really, long post and here it is now in front of you.
Preon
10 ^ -18 metres
In particle physics, preons are point particles, conceived of as sub-components of quarks and leptons. The word was coined by Jogesh Pati and Abdus Salam, in 1974.
Quark
They are considered point like entities with zero size
A quark is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks, down quarks and electrons.
Proton
10 ^ -15 metres
A proton is a subatomic particle, symbol p or p⁺ , with a positive
electric charge of +1e elementary charge and a mass slightly less than
that of a neutron. Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately
one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons".
0.00000000011 m
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1.
Hydrogen is the lightest element in the periodic table. At standard
conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula H₂.
It is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible.
0.00000000034 m
Carbon is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is
nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form
covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table.
Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust.
0.0000000009 m
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C₆H₁₂O₆. Glucose is
the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates.
Amino Acid
0.0000000011 X 0.0000000007 metres
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (–NH2) and carboxyl (–COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N), although other elements are found in the side chains of
certain amino acids.
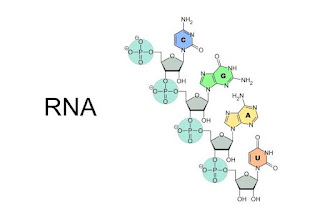
Nucleotide
0.0000000013 x 0.00000000076 metres
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a
phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers –
deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid, both of which are essential
biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth.
0.000000007 metres
Ribonucleic acid is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological
roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and
deoxyribonucleic acid are nucleic acids.
Antibody
0.000000012 m
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large, Y-shaped
protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign
objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a
unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen.
Ribosomes
0.00000003 m
Ribosomes are macromolecular machines, found within all living cells,
that perform biological protein synthesis. Ribosomes link amino acids
together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules
to form polypeptide chains.
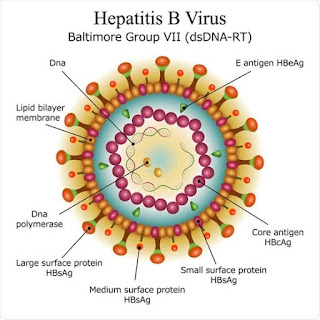
0.000000045 m
A serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus that's
easily preventable by a vaccine.
This disease is most commonly spread by exposure to infected bodily
fluids.
Symptoms are variable and include yellowing of the eyes, abdominal
pain and dark urine. Some people, particularly children, don't
experience any symptoms. In chronic cases, liver failure, cancer or
scarring can occur.
The condition often clears up on its own. Chronic cases require
medication and possibly a liver transplant.
Coated Vesicle
0.00000009 m
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of
coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1976.
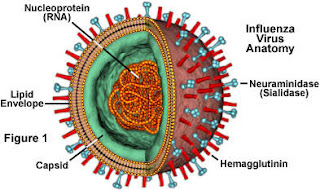
Influenza
0.00000013 m
Influenza, commonly called "the flu", is an infectious disease caused
by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include
fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and
fatigue. These symptoms typically begin 1–4 days after exposure to the
virus and last for about 2–8 days.
X chromosome
0.000007 m
The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes in humans (the other is the Y chromosome). The sex chromosomes form one of the 23 pairs of human chromosomes in each cell. The X chromosome spans about 155 million DNA building blocks (base pairs) and
represents approximately 5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Red blood cell
0.000008 m
Red blood cells, also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles,
haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes, are the most common type of
blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen to
the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system.
Skin cell
0.00003 m
The epidermis has three main types of cell: Keratinocytes (skin cells) Melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) Langerhans cells (immune cells).
Human Egg
0.00013 m
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms
(organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, "female" gamete and a smaller, "male" one). The term is used when
the female gamete is not capable of movement (non-motile).
Amoeba
0.0005 m
Amoeba proteus, of which Chaos diffluens is one of many synonyms, is a
large amoeba related to another genus of giant amoebae, Chaos. It can be
bought at science supply stores. This protozoan uses extensions called
pseudopodia to move and to eat smaller unicellular organisms.
Grain of salt
0.0005 m
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride, a chemical
compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a
natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is
present in vast quantities in seawater.
Grasshopper
0.05 m
Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera.
They are among what is probably the most ancient living group of chewing
herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million
years ago.
Monarch butterfly
0.1 m
The monarch butterfly or simply monarch is a milkweed butterfly in the
family Nymphalidae. Other common names, depending on region, include
milkweed, common tiger, wanderer, and black veined brown. It may be the
most familiar North American butterfly, and is considered an iconic
pollinator species.
Bullfrog
0.15 m
The American bullfrog, often simply known as the bullfrog in Canada and
the United States, is a large true frog native to eastern North America.
It typically inhabits large permanent water bodies such as swamps, ponds,
and lakes.
Great Horned Owl
0.69 m
The great horned owl, also known as the tiger owl, or the hoot owl, is a
large owl native to the Americas. It is an extremely adaptable bird with a
vast range and is the most widely distributed true owl in the
Americas.
Human
Early modern human or anatomically modern human are terms used to
distinguish Homo sapiens that are anatomically consistent with the range
of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from extinct archaic human
species.
Kodiak Bear
3 m
The Kodiak bear, also known as the Kodiak brown bear, sometimes the
"Alaskan brown bear", inhabits the islands of the Kodiak Archipelago in
southwest Alaska. It is the largest recognized subspecies or population of
the brown bear, and one of the two largest bears alive today, the other
being the polar bear.
African Elephant
4 m tall
The African elephant is a genus comprising two living elephant species,
the African bush elephant and the smaller African forest elephant. Both
are social herbivores with grey skin, but differ in the size and color of
their tusks and in the shape and size of their ears and skulls.
Giraffe
6 m tall
The giraffe is an African artiodactyl mammal, the tallest living
terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant. It is traditionally
considered to be one species, Giraffa camelopardalis, with nine
subspecies.
Reticulated Python
8.7 m long
Python is a genus of constricting snakes in the Pythonidae family native
to the tropics and subtropics of the Eastern Hemisphere. The name Python
was proposed by François Marie Daudin in 1803 for non-venomous flecked
snakes. Currently, 10 python species are recognized as valid taxa.
Tyrannosaurus Rex
12.8 m long
Tyrannosaurus is a genus of tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaur. The species
Tyrannosaurus rex, often called T. rex or colloquially T-Rex, is one of
the best represented of these large theropods. Tyrannosaurus lived
throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island
continent known as Laramidia.
Apatosaurus
23 m long
Apatosaurus is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur that lived in
North America during the Late Jurassic period. Othniel Charles Marsh
described and named the first-known species, A. ajax, in 1877, and a
second species, A. louisae, was discovered and named by William H. Holland
in 1916.
Blue whale
30 m long
The blue whale is a marine mammal belonging to the baleen whale parvorder
Mysticeti. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 metres and weighing
up to 199 tonnes, it is the largest animal known to have existed.
Statue of Liberty
93 m tall
The Statue of Liberty is a colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty
Island in New York Harbor within New York City, in the United
States.
Washington monument
169 m tall
The Washington Monument is an obelisk within the National Mall in
Washington, D.C., built to commemorate George Washington, once
commander-in-chief of the Continental Army in the American Revolutionary
War and the first President of the United States.
Gateway Arch
169 m
The Gateway Arch is a 630-foot (192 m) monument in St. Louis, Missouri, United States. Clad in stainless steel and built in the form of
a weighted catenary arch, it is the world's tallest arch, the tallest man-made monument in the Western Hemisphere, and Missouri's tallest accessible building. Built as a monument to the westward expansion of the United States, and officially dedicated to "the American people," the Arch,
commonly referred to as "The Gateway to the West" is the centerpiece
of Gateway Arch National Park and has become an internationally recognized symbol of St. Louis, as well as a popular tourist destination.
Eiffel Tower

324 m
The Eiffel Tower is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in
Paris, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose
company designed and built the tower.
Empire state building
443 m tall
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown
Manhattan in New York City, United States. It was designed by Shreve, Lamb
& Harmon and built from 1930 to 1931. Its name is derived from "Empire
State", the nickname of the state of New York.
Willis Tower
527 m tall
The Willis Tower is a 108-story, 1,450-foot skyscraper in Chicago. The
tower has 108 stories as counted by standard methods, though the
building's owners count the main roof as 109 and the mechanical penthouse
roof as 110.
Burj Khalifa
829.84 m tall
The Burj Khalifa, known as the Burj Dubai prior to its inauguration in
2010, is a skyscraper in Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
Mount Rushmore
1745 m tall
Mount Rushmore National Memorial is a massive sculpture carved into Mount
Rushmore in the Black Hills region of South Dakota. Completed in 1941
under the direction of Gutzon Borglum and his son Lincoln, the sculpture's
roughly 60-ft.-high granite faces depict U.S. presidents George
Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Theodore Roosevelt and Abraham Lincoln. The
site also features a museum with interactive exhibits.
Mt. Fuji
3776 m tall
Japan’s Mt. Fuji is an active volcano about 100 kilometers southwest of
Tokyo. Commonly called “Fuji-san,” it’s the country’s tallest peak, at
3,776 meters. A pilgrimage site for centuries, it’s considered one of
Japan’s 3 sacred mountains, and summit hikes remain a popular activity.
Its iconic profile is the subject of numerous works of art, notably Edo
Period prints by Hokusai and Hiroshige.
Mount McKinley
6196 m tall
Denali is the highest mountain peak in North America, with a summit
elevation of 20,310 feet above sea level. With a topographic prominence of
20,194 feet and a topographic isolation of 4,621.1 miles, Denali is the
third most prominent and third most isolated peak on Earth, after Mount
Everest and Aconcagua.
Mount Everest
8848 m tall
Mount Everest is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the
Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border runs
across its summit point. Its elevation of 8,848.86 m was most recently
established in 2020 by the Nepali and Chinese authorities.
Washington DC
16000 m from sides
Washington, DC, the U.S. capital, is a compact city on the Potomac River,
bordering the states of Maryland and Virginia. It’s defined by imposing
neoclassical monuments and buildings – including the iconic ones that
house the federal government’s 3 branches: the Capitol, White House and
Supreme Court. It's also home to iconic museums and performing-arts venues
such as the Kennedy Center.
Rhode Island
60000 X 77000 m
Rhode Island, a U.S. state in New England, is known for sandy shores and
seaside Colonial towns. It's home to several large cities, including
Newport, which is famed for sailing and Gilded Age mansions, such as The
Breakers. Providence, its capital, is home to Brown University, green
Roger Williams Park, landscaped Waterplace Park and Riverwalk, with the
famed WaterFire art installation.
Israel
114000 X 424000 m
Israel, a Middle Eastern country on the Mediterranean Sea, is regarded by
Jews, Christians and Muslims as the biblical Holy Land. Its most sacred
sites are in Jerusalem. Within its Old City, the Temple Mount complex
includes the Dome of the Rock shrine, the historic Western Wall, Al-Aqsa
Mosque and the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. Israel's financial hub, Tel
Aviv, is known for its Bauhaus architecture and beaches.
Texas
1244000 X 1270000 m
Texas is a state in the South Central region of the United States. It is
the second largest U.S. state by both area and population.
Australia
3999210 m across
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign
country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of
Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in
Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country
Europa (Jupiter's moon)
3138000 m diameter
Europa, or Jupiter II, is the smallest of the four Galilean moons
orbiting Jupiter, and the sixth-closest to the planet of all the 79 known
moons of Jupiter. It is also the sixth-largest moon in the Solar
System.
Ganymede
5268000 m diameter
Ganymede, a satellite of Jupiter, is the largest and most massive of the
Solar System's moons. The ninth-largest object of the Solar System, it is
the largest without a substantial atmosphere. It has a diameter of 5,268
km, making it 26% larger than the planet Mercury by volume, although it is
only 45% as massive.
Pluto
2315000 m diameter
Pluto is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of bodies beyond the
orbit of Neptune. It was the first and the largest Kuiper belt object to
be discovered. After Pluto was discovered in 1930, it was declared to be
the ninth planet from the Sun.
Mercury
4880000 m diameter
Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System and the closest to the
Sun. Its orbit around the Sun takes 87.97 Earth days, the shortest of all
the Sun's planets.
Mars
6794000 m diameter
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in
the Solar System, being larger than only Mercury. In English, Mars carries
the name of the Roman god of war and is often referred to as the "Red
Planet".
Venus
12104000 m diameter
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is named after the Roman
goddess of love and beauty. As the brightest natural object in Earth's
night sky after the Moon, Venus can cast shadows and can be, on rare
occasions, visible to the naked eye in broad daylight.
Earth
12742000 m diameter
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor and support life. About 29.2% of Earth's surface is land consisting of continents and
islands. The remaining 70.8% is covered with water, mostly by oceans, seas, gulfs, and other salt-water bodies, but also by lakes, rivers, and other
freshwater, which together constitute the hydrosphere. Much of Earth's polar regions are covered in ice. Earth's outer layer is divided into several
rigid tectonic plates that migrate across the surface over many millions of years, while
its interior remains active with a solid iron inner core, a liquid outer core that generates Earth's magnetic field, and a convective mantle that drives plate tectonics.
Neptune
49532000 m diameter
Neptune is the eighth and farthest-known Solar planet from the Sun. In
the Solar System, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter, the
third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times
the mass of Earth, slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus.
Uranus
51118000 m diameter
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the
Greek god of the sky, Uranus, who, according to Greek mythology, was the
great-grandfather of Ares, grandfather of Zeus and father of Cronus. It
has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass
in the Solar System.
Saturn
120536000 m diameter
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the
Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of
about nine and a half times that of Earth. It only has one-eighth the
average density of Earth; however, with its larger volume, Saturn is over
95 times more massive.
Jupiter
142984000 m diameter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar
System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that
of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less
than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun.
Pollux
11000000000 m diameter
Pollux, designated β Geminorum, is an orange-hued evolved giant star
about 34 light-years from the Sun in the constellation of Gemini. It is
the brightest star in Gemini and the closest giant star to the Sun.
Arcturus
36000000000 m diameter
Arcturus, designation α Boötis, is the brightest star in the
constellation of Boötes, the fourth-brightest in the night sky, and the
brightest in the northern celestial hemisphere
Aldebaran
61000000000 m diameter
Aldebaran, designated α Tauri, is a giant star measured to be about 65
light-years from the Sun in the zodiac constellation Taurus. It is the
brightest star in Taurus and generally the fourteenth-brightest star in
the night sky, though it varies slowly in brightness between magnitude
0.75 and 0.95.
Rigel
110000000000 m diameter
Rigel, designated β Orionis, is a blue supergiant star in the
constellation of Orion, approximately 860 light-years from Earth. Rigel is
the brightest and most massive component – and the eponym – of a star
system of at least four stars that appear as a single blue-white point of
light to the naked eye.
Antares
1200000000000 m diameter
Antares, designated α Scorpii, is on average the fifteenth-brightest star
in the night sky, and the brightest object in the constellation of
Scorpius. Distinctly reddish when viewed with the naked eye, Antares is a
slow irregular variable star that ranges in brightness from apparent
magnitude +0.6 to +1.6.
Betelgeuse
1600000000000 m diameter
Betelgeuse is usually the tenth-brightest star in the night sky and,
after Rigel, the second-brightest in the constellation of Orion. It is a
distinctly reddish semiregular variable star whose apparent magnitude,
varying between +0.0 and +1.6, has the widest range displayed by any
first-magnitude star.
Mu cephei
2300000000000 m diameter
Mu Cephei, also known as Herschel's Garnet Star, Erakis, or HD 206936, is
a red supergiant or hypergiant star in the constellation Cepheus. It
appears garnet red and is located at the edge of the IC 1396 nebula.
VV Cephei A
2600000000000 M DIAMETER
VV Cephei, also known as HD 208816, is an eclipsing binary star system
located in the constellation Cepheus, approximately 5,000 light years from
Earth. It is both a B[e] star and shell star. VV Cephei is an eclipsing
binary with the second longest known period.
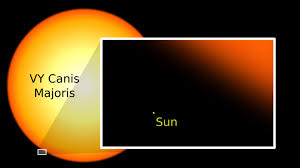
VY canis majoris
3000000000000 m diameter
VY Canis Majoris is an extreme oxygen-rich red hypergiant or red
supergiant and pulsating variable star 1.2 kiloparsecs from the solar
system in the slightly southern constellation of Canis Major.
Solar system
30000000000000 m
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the
objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of the objects that
orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the eight planets, with the
remainder being smaller objects, the dwarf planets and small Solar System
bodies.
Homunculus Nebula
200000000000000 m
The Homunculus Nebula is a bipolar emission and reflection nebula
surrounding the massive star system Eta Carinae, about 7,500 light-years
from Earth. The nebula is embedded within the much larger Carina Nebula, a
large star-forming H II region.
Stingray Nebula
1510000000000000 m
The Stingray Nebula is the youngest known planetary nebula. The Stingray
is located in the direction of the southern constellation Ara, and is
located 18,000 light-years away.
Cat's Eye Nebula
3780000000000000 m
The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation
of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786.
Crab nebula
104000000000000000 m
The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the
constellation of Taurus. The common name comes from William Parsons, 3rd
Earl of Rosse, who observed the object in 1842 using a 36-inch telescope
and produced a drawing that looked somewhat like a crab.
Orion Nebula
189000000000000000 m
The Orion Nebula is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being
south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the
brightest nebulae and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. It is
1,344 ± 20 light-years away and is the closest region of massive star
formation to Earth.
Rosette Nebula
1230000000000000000 m
The Rosette Nebula is an H II region located near one end of a giant
molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy. The open
cluster NGC 2244 is closely associated with the nebulosity, the stars of
the cluster having been formed from the nebula's matter.
Omega Centauri
1660000000000000000 m
Omega Centauri is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus
that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in
1677. Located at a distance of 17,090 light-years, it is the largest known
globular cluster in the Milky Way at a diameter of roughly 150
light-years.
Tarantula Nebula
6150000000000000000 m
The Tarantula Nebula is an H II region in the Large Magellanic Cloud,
from the Solar System's perspective forming its south-east corner.
Small Magellanic Cloud
66200000000000000000 m
The Small Magellanic Cloud, or Nubecula Minor, is a dwarf galaxy near the
Milky Way. Classified as a dwarf irregular galaxy, the SMC has a diameter
of about 7,000 light-years, contains several hundred million stars, and
has a total mass of approximately 7 billion solar masses.
Large Magellanic Cloud
132000000000000000000 m
The Large Magellanic Cloud is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a
distance of around 50 kiloparsecs, the LMC is the second or third closest
galaxy to the Milky Way, after the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal and the
possible dwarf irregular galaxy known as the Canis Major
Overdensity.
Triangulum Galaxy
473000000000000000000 m
The Triangulum Galaxy is a spiral galaxy 2.73 million light-years from
Earth in the constellation Triangulum. It is catalogued as Messier 33 or
NGC 598. The Triangulum Galaxy is the third-largest member of the Local
Group of galaxies, behind the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way.
Milky way galaxy
1140000000000000000000 m diameter
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name
describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen
in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually
distinguished by the naked eye.
Andromeda Galaxy
2080000000000000000000 m diameter
The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and
originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy approximately
2.5 million light-years from Earth and the nearest major galaxy to the
Milky Way.
NGC 4889
4730000000000000000000 m diameter
NGC 4889 is an E4 supergiant elliptical galaxy. It was discovered in 1785
by the British astronomer Frederick William Herschel I, who catalogued it
as a bright, nebulous patch. The brightest galaxy within the northern Coma
Cluster, it is located at a median distance of 94 million parsecs from
Earth.
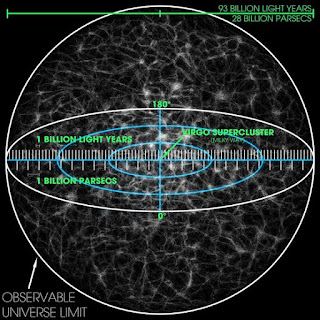
Virgo Supercluster
1040000000000000000000000 m
The Virgo Supercluster or the Local Supercluster is a mass concentration
of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which in turn
contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies. At least 100 galaxy groups
and clusters are located within its diameter of 33 megaparsecs.
Horologium supercluster
5200000000000000000000000 m
The Horologium-Reticulum Supercluster, is a massive supercluster
spanning around 550 million light-years. It has a mass of around 10¹⁷
solar masses, similar to that of the Laniakea Supercluster, which
houses the Milky Way.
Local universe
24600000000000000000000000 m diameter
Studies of the nearby universe encompass a region of approximately 1 billion light years in
radius, over which the effects of cosmic evolution are small. Within
this volume galaxies and associated objects are essentially frozen in
their present day configurations.
Observable universe
880000000000000000000000000 m diameter
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present
time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the cosmological expansion. There may be 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe, although that number has recently been estimated at only several
hundred billion based on new data from New Horizons. Assuming the universe is isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is
roughly the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe has
a spherical volume (a ball) centered on the observer. Every location in the universe has its own
observable universe, which may or may not overlap with the one centered on
Earth.